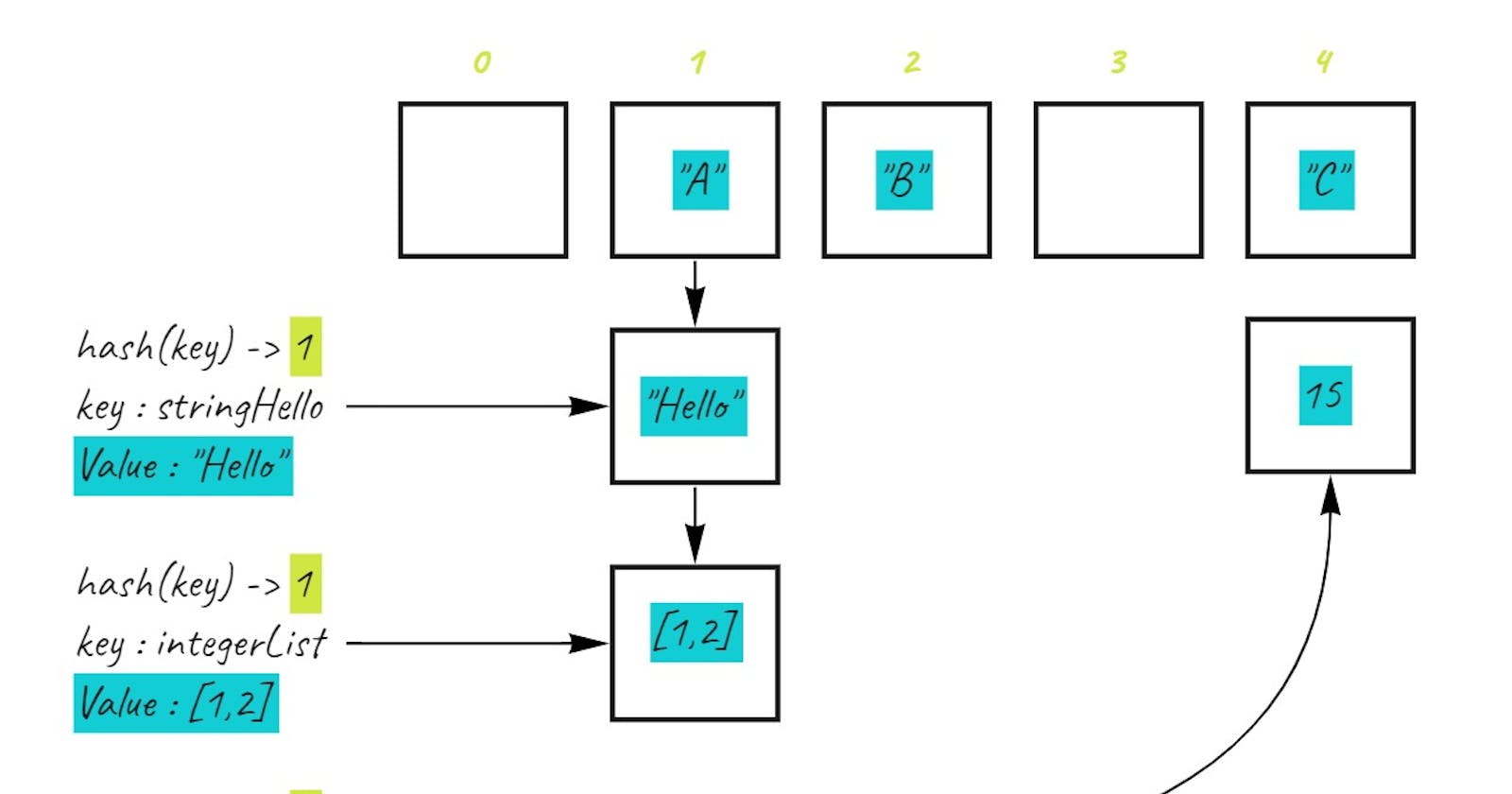
What are Hashtables?
Hashtables are a type of data structures that stores data as key-value pairs. This means every Node or Bucket has both a key, and a value. Hashing can also be defined as a technique that is used to uniquely identify a specific object from a group of similar objects.
Hashtables Components
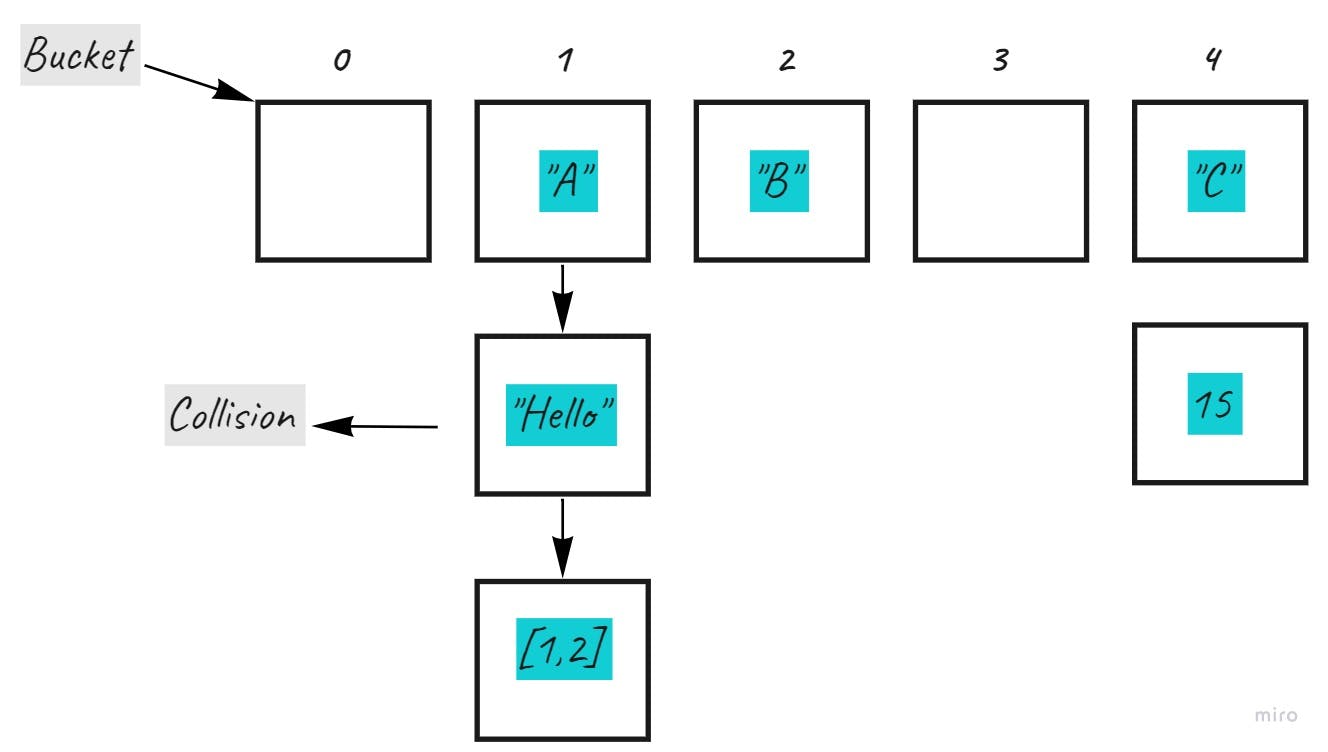
1. Buckets
A bucket is what is contained in each index of the array of the hashtable. Each index is a bucket. An index could potentially contain multiple key-value pairs if a collision occurs.
2. Collisions
A collision is what happens when more than one key gets hashed to the same location of the hashtable.
3. Hash
A hash is the result of some algorithm taking an incoming string and converting it into a value that could be used for either security or some other purpose. In the case of a hashtable, it is used to determine the index of the array.
- The result (hash) is the index of the key-value pair in the hash table.
Pros & Cons of Hash Tables
- Can hold keys of many data types as long as they're hashTable.
- Worst case time complexity of Access, Insert, Delete or Search are O(n).
- Hard to look for maximum and minimum values.
- requesting a value with a given key takes O(1).
- requesting a key from a given value takes O(n).
Internal Methods
Add()
- send the key to the GetHash method.
- Once you determine the index of where it should be placed, go to that index
- Check if something exists at that index already, if it doesn’t, add it with the key/value pair.
- If something does exist, add the new key/value pair to the data structure within that bucket.
Find()
- The Find takes in a key, gets the Hash, and goes to the index location specified.
- Once the index location is found in the array.
- The algorithm iterates through the bucket and see if the key exists and return the value.
Contains()
- The Contains method will accept a key, and return a bool on if that key exists inside the hashtable.
- The best way to do this is to have the contains call the GetHash and check the hashtable if the key exists in the table given the index returned.
GetHash()
- The GetHash will accept a key as a string
- conduct the hash.
- Return the index of the array where the key-value should be placed.
Implementation
Creating the Hashtmap class
- Initializing an object through init method and giving it a size attribute (this size it not static you can put any size you want --> it represents the size of the list that will be created )
- Another attribute (map) to create the list of the provided size.
class HashTable:
def __init__(self, size = 1024):
self.size = size
self.map = [None]*size
Hash method
- This method takes a stirng key as an argument and returns its hashed value according to ASCII
def hash(self, key):
ascii_sum = 0
for char in key:
ascii_char = ord(char)
ascii_sum += ascii_char
hashed = (ascii_sum * 19) % self.size
return hashed
Set method
- This method sets key-value pairs at the hashed bucket (list) if it was empty or adds them as collisions if it wasn't.
- it also updates the key value if it was passed with another value.
def set(self, key, value):
// return hashed value which is the index of the key
hashed = self.hash(key)
if self.map[hashed] is None:
self.map[hashed] = [[key, value]]
else:
self.map[hashed].append([key, value])
Get method
- This method takes a key and returns the value associated with that key in the map
def get(self, key):
hashed = self.hash(key)
return self.map[hashed]
Contains method
- This method return True if the hashmap contains a specific key, and false if it doesn't
def contains(self, key):
if self.map[self.hash(key)]:
return True
else:
return False
keys method
- This method returns a new list with all keys in the hashmap
def keys(self):
lst = []
for i in self.map:
if i:
[lst.append(index[0]) for index in i]
return lst